AI in Healthcare: Key Use Cases and Benefits

Artificial Intelligence is becoming a staple in today’s healthcare. From enhancing patient outcomes to streamlining hospital operations, AI makes a real daily impact. It helps doctors diagnose diseases more accurately. And it makes patient care smoother and more personalized. This article details how exactly AI is used in healthcare and the benefits it brings. It provides insights to help you use AI effectively in your practice or organization.
Key Points
|
Key Use Cases of AI in Healthcare and Their Benefits
Medical Diagnosis and Predictive Analytics
AI is changing medical diagnosis with advanced tools and real-time data analysis. For example, AI-powered microscopes can find subtle patterns in medical images that humans might miss. This leads to more accurate diagnoses and faster decisions. AI predictive models analyze patient data to identify those at risk of certain conditions. This allows for preventive care strategies that can save lives and reduce costs.
Benefits
- Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy: AI reduces errors by analyzing complex medical data more precisely than traditional methods. For example, AI algorithms can detect subtle patterns in imaging data, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses of diseases like cancer and heart conditions.
- Early Disease Detection: AI systems monitor patient data continuously, spotting early signs of diseases. This allows for timely interventions, improving patient outcomes and lowering treatment costs.
- Predictive Healthcare: AI models can predict the likelihood of diseases based on medical history and lifestyle factors. This helps healthcare providers offer personalized preventive measures, improving patients’ quality of life.
Example: Using AI to Analyze Medical Images
Aidoc, an Israeli-based tech company, provides an AI-powered platform for analyzing medical images. The platform helps radiologists detect abnormalities and prioritize urgent cases. Thus, it improves diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. By integrating AI into radiology workflows, Aidoc ensures that critical cases are identified quickly and no urgent case is overlooked.
Drug Discovery and Development
AI speeds up the drug discovery process by finding potential drug candidates faster. By analyzing large datasets, AI can predict how different compounds will interact with targets. This streamlines the identification of promising candidates for further testing. AI also helps develop new treatments from existing drugs, offering solutions to unmet medical needs.
Benefits
- Accelerated Drug Discovery: AI cuts down the time needed to bring new drugs to market by quickly analyzing vast datasets. This speed is crucial during urgent health crises like pandemics.
- Cost Efficiency: By automating stages of drug development, AI reduces costs associated with traditional methods. This makes it possible for companies to invest in more innovative research.
- Innovative Treatments: AI leads to breakthroughs in treatments through advanced research methods. By analyzing genetic and clinical data, AI uncovers new therapeutic targets, leading to treatments that were previously unimaginable.
Example: Using AI for Drug Discovery and Clinical Trial Optimization
Owkin uses AI to find new treatments, optimize clinical trials, and develop AI diagnostics. They work with pharmaceutical companies to enhance therapeutic programs. Their approach speeds up the discovery of effective drugs and makes clinical trials more efficient and targeted. Owkin’s AI platform analyzes large amounts of data to predict how different patients will respond to treatments, personalizing and improving clinical trials.
Robotic Surgery and AI-Driven Procedures
Robotic technologies improve surgical precision and allow for minimally invasive procedures. AI-driven surgical tools contribute to better patient outcomes and increased safety during operations. By providing real-time feedback and assistance, AI helps surgeons perform complex procedures more accurately. This reduces recovery times and lowers the risk of complications.
Benefits
- Increased Surgical Precision: AI enhances the accuracy of surgeries by providing real-time guidance to surgeons. This reduces recovery times and minimizes surgical complications.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: AI-driven tools enable less invasive surgeries, leading to smaller incisions and shorter hospital stays. Patients recover faster, and healthcare costs are lower.
- Improved Patient Safety: AI technologies in robotic surgery ensure higher success rates and safer procedures. By assisting with precise movements and monitoring, AI reduces the chance of human error.
Example: An AI-Driven Software for Surgical Planning and Navigation
Brainlab develops software for planning and navigating surgeries, including image-guided surgery and robotic assistance. This improves surgical precision and patient outcomes by helping surgeons plan complex procedures more accurately. Brainlab’s AI solutions work with existing surgical equipment, enhancing surgical teams’ tools for better patient care.
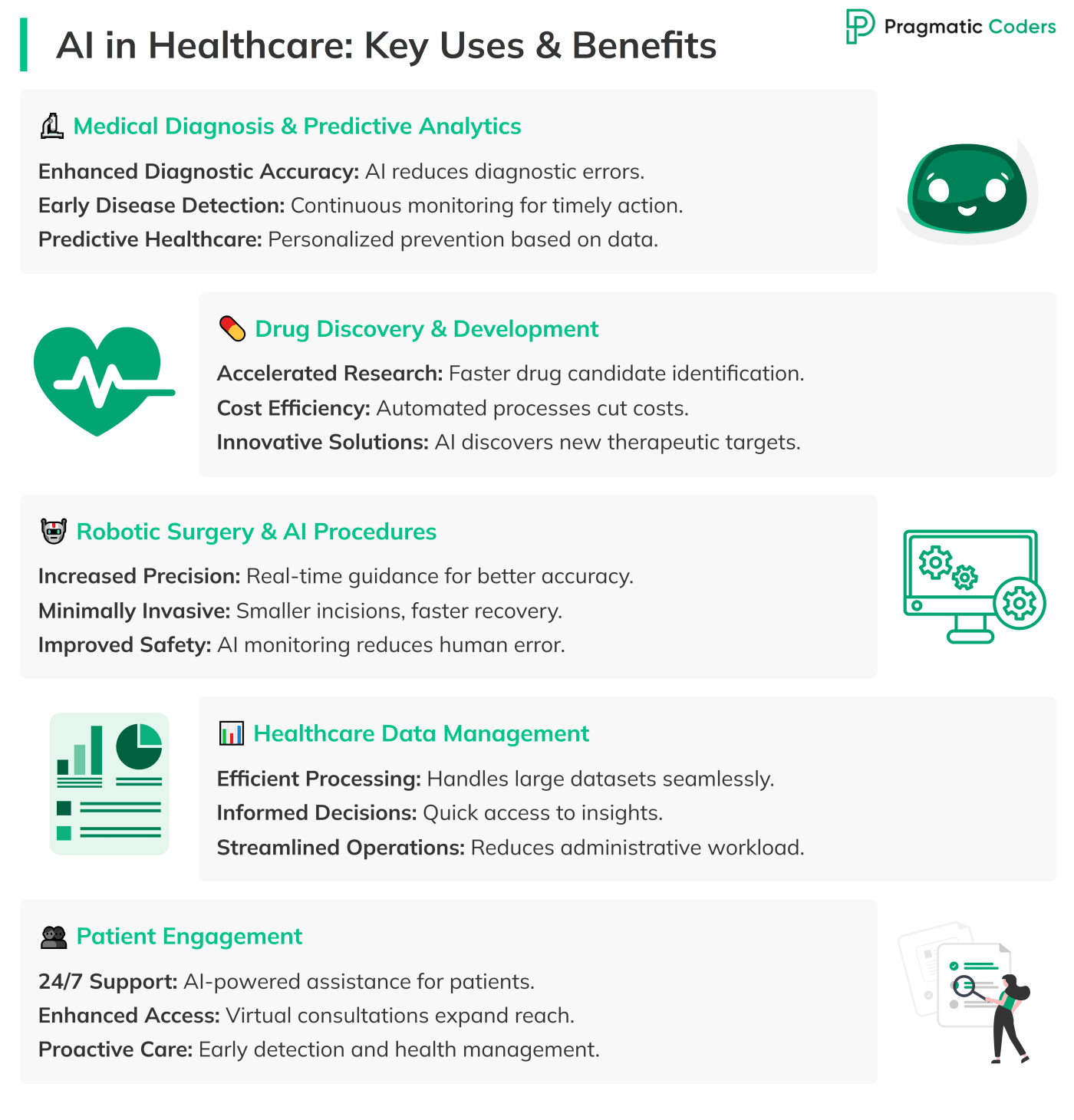
Healthcare Data Management and Clinical Intelligence
AI efficiently manages vast amounts of patient data by bringing together different data sources and providing actionable insights. AI decision-making tools improve clinical workflows and operational efficiency in healthcare facilities. By using AI, healthcare providers can make informed decisions quickly, leading to better patient care and optimal use of resources.
Benefits
- Efficient Data Handling: AI manages large datasets smoothly, improving data access and usability. This ensures healthcare providers have quick access to needed information, reducing treatment delays.
- Informed Decision-Making: AI provides actionable insights by analyzing patient data and spotting trends. This enhances clinical workflows, enabling timely decisions that benefit patient care.
- Operational Efficiency: AI streamlines data management processes, reducing administrative burdens. This allows healthcare staff to focus more on patient care, making the healthcare system more effective.
Example: AI-Driven Analytics for Medicine Availability
Johnson & Johnson’s Medical Engagement.ai leverages AI-driven analytics to identify unmet medical needs by analyzing real-world clinical data and inputs. It enables Medical Science Liaisons to collaborate with physicians and institutions. This collaboration ensures that patients receive the most effective treatments based on the latest clinical guidelines.
Patient Engagement and Experience Enhancement
AI-powered chatbots and virtual visits improve patient support and access to healthcare services. AI symptom checkers empower patients to manage their health proactively. By providing personalized interactions and easy access to medical advice, AI enhances the patient experience and fosters a more connected healthcare environment.
Benefits
- Improved Patient Support: AI provides 24/7 assistance and personalized interactions, enhancing patient satisfaction. Patients get immediate responses, reducing wait times and feeling more supported.
- Enhanced Accessibility: AI enables virtual consultations, making healthcare more accessible to more people. This benefits individuals in remote or underserved areas who might face barriers to accessing care.
- Proactive Health Management: AI helps detect symptoms early and empowers patients to manage their health proactively. By offering tools for self-monitoring and early intervention, AI helps patients take charge of their health.
Example: Using AI to Automate and Personalize Patient Interactions
Notable Health uses AI to automate and personalize patient interactions like scheduling, reminders, intake, and follow-up communications. Their platform aims to improve patient satisfaction and operational efficiency by streamlining administrative tasks. By handling routine interactions, Notable Health allows healthcare providers to focus more on patient care, enhancing both efficiency and service quality.
Challenges and Drawbacks of Implementing AI in Healthcare
Ethical and Data Privacy Concerns
- Addressing Bias and Discrimination
Ensuring AI algorithms are fair and unbiased is crucial to prevent discrimination in healthcare outcomes. Bias can come from skewed training data or flawed designs, leading to unequal treatment for different patient groups. To reduce biases, it’s important to use diverse datasets, perform regular fairness audits, and include ethical guidelines in AI development.
- Data Privacy and Security
Protecting sensitive patient information from breaches is vital. AI systems often need access to large amounts of personal health data, making privacy and security key concerns. Following data protection regulations ensures that patient data is handled securely. Implementing strong encryption, access controls, and regular security checks are essential to safeguard information.
- Intellectual Property (IP) Protection
Beyond safeguarding patient data, protecting intellectual property is equally critical in healthcare AI. A growing share of MedTech value resides in proprietary algorithms that must be shielded from theft or misuse. Leaving IP exposed—whether in offline desktop apps or unsecured environments—raises the risk of piracy, reverse engineering, and compliance failures. The most effective defense is to keep algorithms server-side whenever possible, with layered safeguards only when offline deployment is unavoidable. Our guide to IP protection in healthcare explains when to choose cloud, when offline is necessary, and how to raise the cost of attacks.
Technological and Operational Limitations
- Current Limitations of AI Technology
Understanding what AI can and cannot do in clinical settings is important. While AI helps in many areas, it still lacks in tasks requiring human judgment and empathy. AI may struggle with unclear or incomplete data, and its effectiveness depends on the quality of input data. It also doesn’t have the intuitive understanding that human healthcare providers bring to patient interactions.
- Human-AI Collaboration Challenges
Making sure healthcare professionals and AI systems work well together requires training and adaptation. Staff need to learn how to use AI tools in their daily work. This involves technical training and fostering a mindset where AI is seen as a helpful tool, not a replacement. Overcoming resistance to change and building trust in AI systems are key for successful collaboration.
Regulatory and Workforce Implications
- Navigating AI Regulations
Following guidelines set by health authorities and regulatory bodies is necessary for the safe use of AI in healthcare. Regulations can affect how quickly AI is implemented, so organizations need to adapt swiftly. Staying updated with regulatory changes and ensuring AI systems meet all legal and ethical requirements is essential to avoid legal issues.
- Potential Job Displacement
Addressing concerns about job changes due to AI integration is important. While AI can automate some tasks, possibly leading to job displacement, it also creates new roles focused on managing AI systems. Strategies for workforce adaptation and upskilling can help reduce the impact on employment. Investing in training programs equips the workforce with the skills needed to succeed in an AI-enhanced environment.
Conclusion
AI is transforming healthcare through its diverse applications. From improving diagnostics to automating healthcare back-office with AI agents, the benefits are substantial. These include better diagnostic accuracy, faster drug discovery, improved surgical precision, efficient data management, and enhanced patient support. However, it’s important to balance innovation with ethical considerations to ensure AI is a tool for better health outcomes.
As AI continues to develop, thoughtful and responsible integration into healthcare will be key to unlocking its full potential. Addressing challenges like bias, data privacy, technological limitations, and workforce implications is crucial for sustainable adoption. By fostering collaboration between AI technologies and human expertise, the healthcare industry can achieve a blend of innovation and compassionate care. This will lead to a healthier and more efficient future for patients and providers alike.








