9 top AI trends to watch in 2026
AI’s big moment in 2026 may come with big questions.
On August 2, the EU AI Act takes full effect. This starts a global race to follow the rules. Are companies ready? Many will need to build or fix their risk and governance systems.
Plus, there’s the infrastructure problem. Bigger models use more energy. Can the industry handle it? There’s a stronger push for green tech and custom hardware. And as data rules get stricter, will “Sovereign AI” – keeping data and computing local – become the new normal?
This report answers these questions and summarizes 9 key trends expected to shape the AI landscape in 2026.
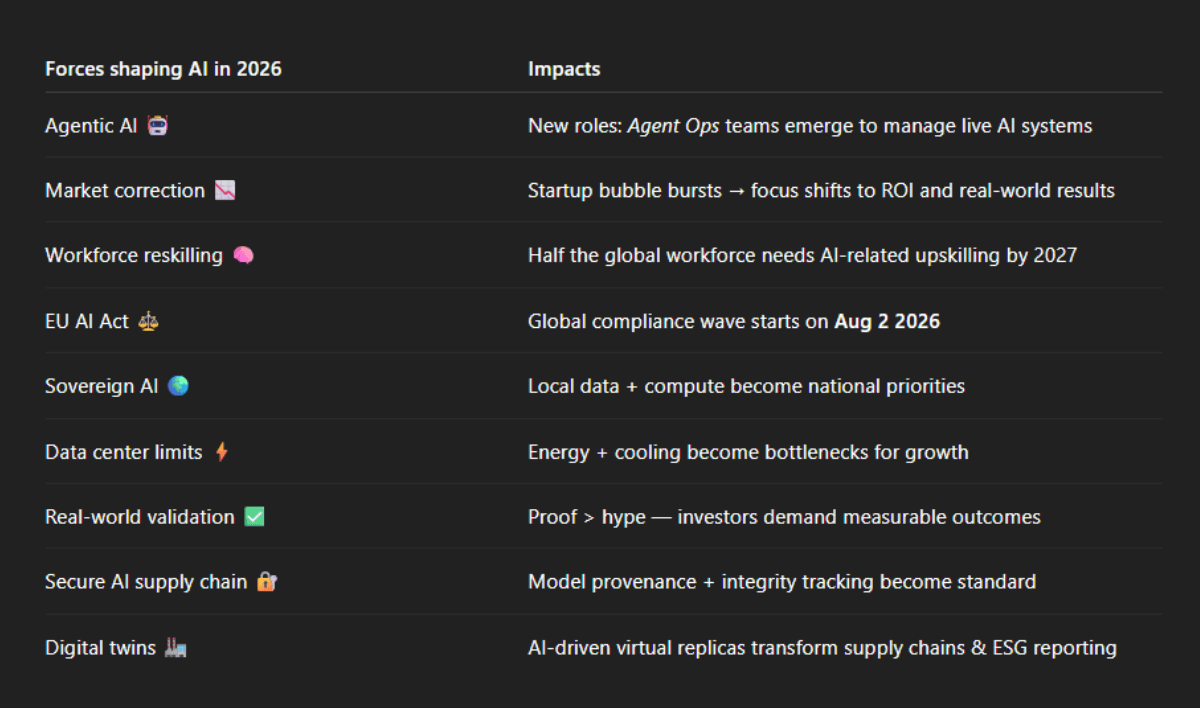
AI in 2026 is shaped by three main forces:
|
1. AgentOps teams are starting to appear
Autonomous systems in production bring a new role: Agent Operations (AgentOps). Agent Ops builds on MLOps but also needs skills in compliance, auditing, and live system control.
Who are AgentOps?
Agent ps roles are related to data and ML engineering but focus more on running and managing AI agents in real time. Here’s what they typically do:
- Deploy agents into live systems
- Monitor behavior (make sure they do what they’re supposed to)
- Handle failures or unexpected actions
- Update or retrain agents when needed
- Ensure agents follow rules and policies (compliance, auditing)
They might work with data engineers, ML engineers, and DevOps, but their job is more about day-to-day operations of autonomous agents
In India alone, analysts estimate over 1 million AI specialists will be needed to fill new roles by 2026. (Et Edge Insights, 2025)
2. Market correction and consolidation

From 2024 to 2025, many startups rushed into the agentic AI space. But:
- Valuations are very high… but it’s an economic bubble. (AIInvest, 2025)
- Total VC funding to AI dropped ~ 40 % year‑over‑year in H1 2025, even though deal value rose. (Ropes & Gray, 2025)
- Big tech and private equity increasingly buy smaller AI firms to absorb talent, IP, and product lines.
So, what might happen in 2026-2027?
- Startups with unclear differentiation or weak business models will struggle to raise more funds and may collapse or get acquired.
- Margins, recurring revenue, and tangible ROI will matter more than hype.
- Vertical consolidation: AI infrastructure, chips, model training, and deployment tools might get merged or integrated.
Also check: What are zombie funds?
3. Workers learn new skills and roles change
AI automation impacts millions of jobs. IT engineers, analysts, and even managers must learn new skills: not only how to use AI but also how to supervise it.
By 2027, more than 50% of workers globally will need reskilling in AI-related fields (World Economic Forum, 2020).
What new skills do people need?
- Technical: prompt engineering, large‑model fine‑tuning, systems integration
- Compliance & ethics: bias detection, audit, regulation awareness
- Monitoring & operations: how to supervise agentic systems, fix failures
- Human‑AI collaboration: deciding what AI should do and when humans step in
- Soft skills: adaptability, critical thinking, communication, oversight
New curricula now combine prompt engineering, bias detection, and regulatory awareness.
The most in-demand roles: AI Product Manager (leads AI projects), AgentOps Engineer (runs AI agents in real time), and Generative AI Developer (codes using AI).
4. EU AI Act: A global compliance deadline
The EU AI Act will fully apply on 2 August 2026. It sets strong rules for companies that offer AI services to people in the EU, even if those companies are based outside Europe.
The law targets both General Purpose AI models and high-risk systems. It requires things like testing, risk monitoring, cybersecurity, and clear documentation. Companies must explain how their models work, keep records of training data, and allow external checks.
Like GDPR changed data privacy laws, the EU AI Act could become a global standard for AI regulation.
Also read:
5. Sovereign AI and regional AI hubs
The term Sovereign AI means AI systems whose data storage and computing happen inside a country, so they comply with local laws and avoid foreign control.
Countries such as France, Japan, and the UAE already fund sovereign data centers and local language models.This trend reflects a growing need for data control and national security in a tense geopolitical environment. What’s more, local models can better reflect language, norms, and values of a region. Plus, many laws require that certain data not leave a country or region.
By 2026, Sovereign AI will be a standard requirement in finance, defense, and healthcare.
In addition to storing AI data inside a country, governments also aim to create regional AI hubs that combine compute capacity, research, and talent development.
Examples: The EU’s “AI Made in Europe” initiative, Saudi Arabia’s $40B AI fund, and Japan’s AI Cloud.
6. The Data Center Energy Crisis

AI is growing so fast that it’s hitting the limits of current global infrastructure.The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that electricity demand from data centers will more than double by 2030, while AI-specific demand may quadruple.
Facts:
- In the U.S., data center energy use could grow by 20–40% as early as 2025.
- New AI facilities under construction consume up to 20× more energy than traditional ones.
- The total energy used by AI systems could soon equal the entire national consumption of Japan.
This reality transforms energy into a strategic asset — as important as compute capacity itself.
To keep up, the industry is turning to sustainable hardware and smarter cooling. Cooling alone uses around 37% of data center power. By 2030, over half of centers will use liquid or hybrid cooling systems. Big tech firms like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon are investing heavily in renewables and low-carbon data centers. Metrics like PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness) are becoming central to measuring efficiency.
Looking ahead, neuromorphic computing — chips designed to work like the human brain — could change everything. These processors promise huge speed with very low power use. While still experimental, they could help AI scale without breaking energy limits.
7. Real-World Validation for VC Investments
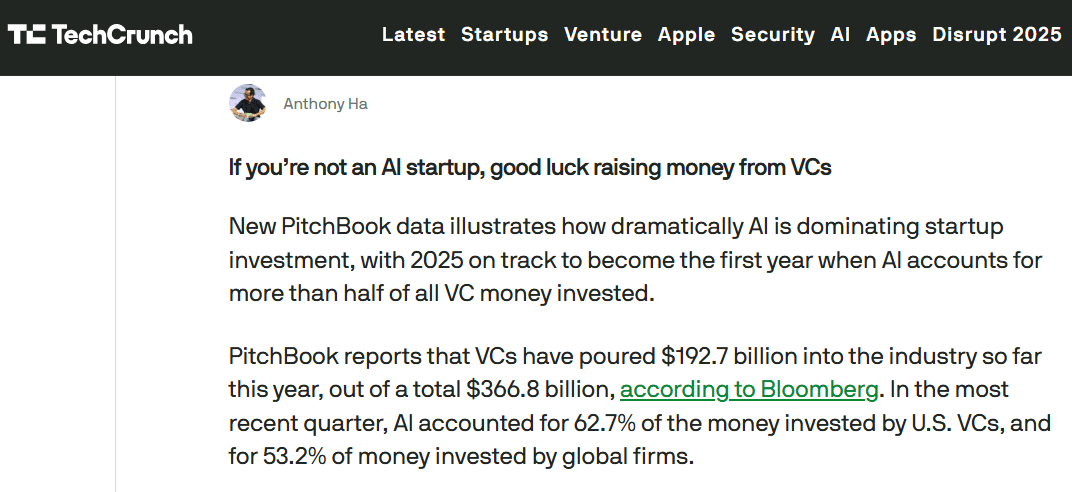
Venture capital is shifting from speculation to proof. By 2026, startups must show real-world results to secure funding. Investors now look for hard metrics: client dependency, uptime reliability, and verified cost savings.
In healthcare, this means only companies with regulatory approval (like FDA clearance) and measurable outcomes – such as reducing clinical trial times by 15–30% – can raise serious capital. In finance, the bar is just as high: compliance and explainability are now essential, not optional.
As a result, VC interest moves from “potential” to proven “irreplaceability.”
At the same time, mergers and acquisitions stay strong despite macroeconomic uncertainty. In fact, nearly 75% of the tech M&A deals in H1 2025 were AI-related transactions. (CORUM, 2025). This shows that private equity and corporations now see AI as critical infrastructure, not just a trend.
Acquirers are targeting companies with specialized talent, sovereign compute access, and valuable IP portfolios – assets they see as necessary to stay competitive.
8. Securing the AI Supply Chain
AI’s growing use of third-party components is creating new cybersecurity risks. Attacks like CloudJacking – where cloud resources are stolen – and tampered model weights are becoming more frequent. Model weights are the core parameters that guide how an AI system works. If they are modified, the model can behave incorrectly or include hidden functions.
To address this, companies are turning to model provenance tracking – a way to record the full history of a model, including how it was trained and handled. This helps detect unwanted changes and build trust in the model. Supply chain audits for large language models are also becoming standard.
By 2026, security strategies will need end-to-end integrity checks – from training data to the final API – to ensure AI systems are secure and reliable.
9. Digital Twins for Supply Chains and ESG
By 2026, Digital Twins — virtual models of physical systems — become standard across manufacturing and logistics.
Combined with AI, these systems simulate operations in real time, optimize maintenance, and track environmental performance.
Because up to 80% of emissions occur in supply chains, digital twins are now central to ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) reporting.
Companies use them to predict risks, test carbon reduction strategies, and improve transparency for regulators.
The catch? Digital twins require clean, real-time, unified data. Most logistics operations carry years of data debt: siloed systems, batch processing, and poor data entry practices that must be addressed before a twin can deliver value.
By 2026, BMW’s Virtual Factory sets a benchmark for digital twin use in manufacturing. It digitally replicates over 30 production sites, linking building data, equipment, logistics, vehicle specs, and 3D simulations of manual tasks into a real-time model of factory operations.
Using NVIDIA Omniverse, planners run detailed virtual tests — like collision checks for parts — without building physical prototypes. Tasks that once took weeks now take days, cutting production planning costs by up to 30%.
Bottom Line
AI isn’t growing unchecked anymore. Now it’s shaped by limits like energy, ethics, and laws. In the next few years, it’s less about what AI can do, and more about how responsibly it actually works in the real world.








