How to Create Lean Canvas for Your Startup

When coming up with your business idea it is important to turn it into a business plan. But getting your thoughts out of your head and into something tangible can be challenging. Developing a traditional business plan can take weeks or months, and although it might be helpful for pitching your business idea, it won’t help in capturing and testing out your ideas.
For this purpose, it is more beneficial to utilize Lean Canvas, a startup-friendly alternative to the business model canvas.
In this article, we will take a look at what is Lean Canvas, why you should use it, and how to fill in the 9 blocks that it consists of.
We fill out Lean Canvas during personalized product discovery sessions.
What is Lean Canvas?
Lean Canvas is a one page business plan for any product idea created by Ash Maurya. This simple but efficient way of describing the business model of your product uses 9 actionable blocks to help you map out important aspects of your business.
The blocks cover the following areas:
- Problem
- Customer Segments
- Key Metrics
- Solution
- Unique Value Proposition
- Unfair advantage
- Channels
- Revenue Streams
- Cost Structure
A quick note before we move on: Lean Canvas is one of the chapters in our free ebook How to start a startup. Be sure to download it!
What is the purpose of Lean Canvas?
The purpose of the Lean Canvas is to facilitate rapid iteration and learning through the validation of a problem-solution fit for early-stage startups.
What is Lean Canvas in Agile?
“What is Lean Canvas in Agile” is a question that pops up quite often in search results. That’s interesting – Lean Canvas isn’t inherently an Agile tool. However, it can be used effectively within the Agile framework because it aligns with its principles:
- Aligns with iterative development
- Supports customer focus
- Matches Agile’s adaptability
So, the answer is: Lean Canvas in Agile is the same as Lean Canvas outside of Agile. 😉
What’s the difference between Lean Canvas and Business Model Canvas?
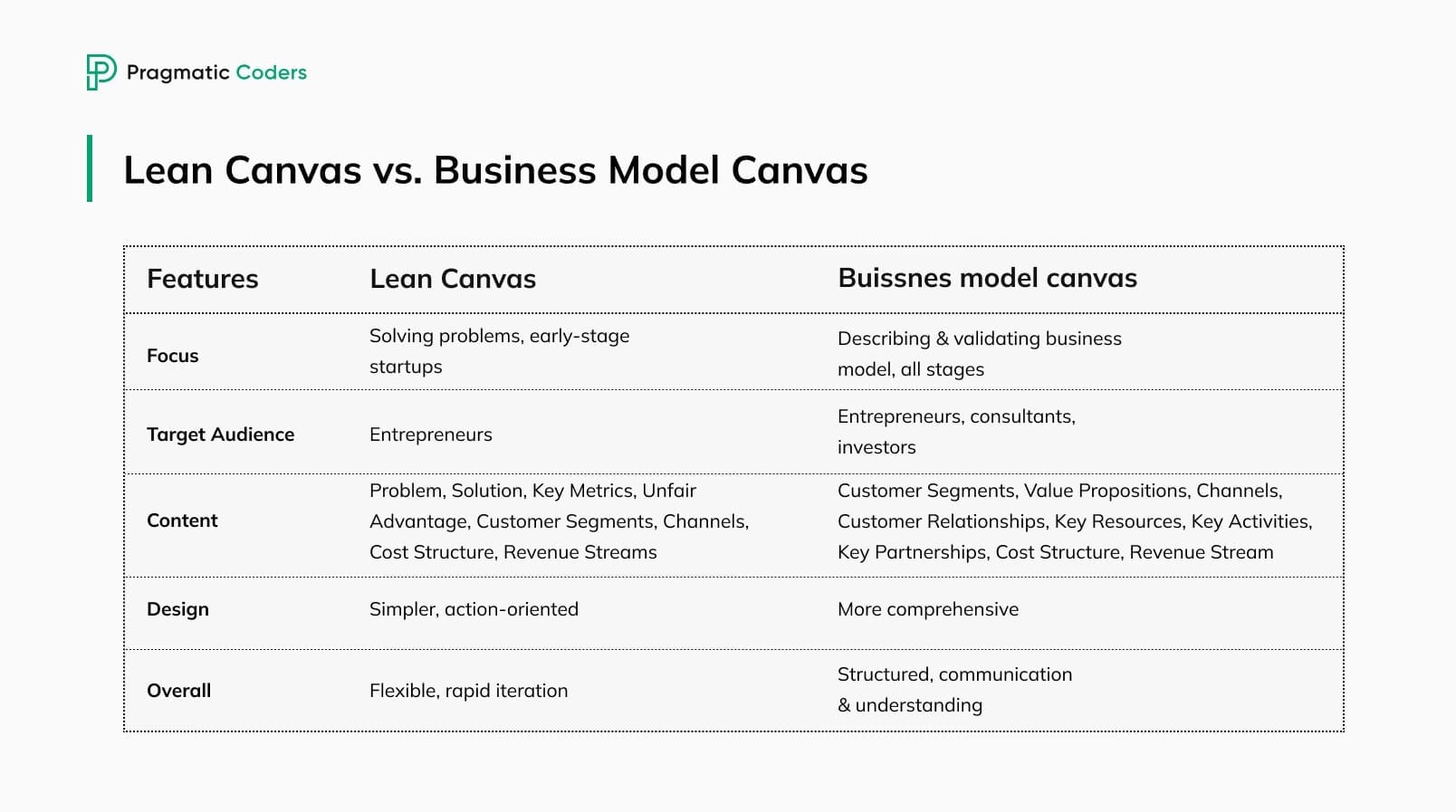
You might have stumbled upon two deceptively similar terms: Lean Canvas and Business Model Canvas. While similar, they’re not the same thing.
Lean Canvas is a variation of the business model canvas (originally created by Alex Osterwalder). It focuses on validating a problem solution fit through rapid iteration, while Business Model Canvas provides a more comprehensive overview of the entire business model – that’s the main difference.
What else sets them apart?
- Lean Canvas focuses on solving problems and learning through the process. It’s a flexible and adaptable tool for rapid iteration and testing, designed for entrepreneurs at the early stages of business development.
- Business Model Canvas, on the other hand, focuses on describing and validating a business model. It’s more comprehensive and structured. It’s widely used by entrepreneurs – but with more advanced businesses.
To sum up, if you’re a startup founder at the beginning of your product journey, choose Lean Canvas; it will be easier to use.
How long should a Lean Canvas be?
A Lean Canvas, by its very nature, is designed to fit on a single page, and take around 20 minutes to complete. This allows for quick and easy visualization of the core business model elements.
There’s no specific “length” requirement, as the canvas itself is a pre-defined size or format. However, the focus should be on capturing essential information within each section.
⬇️ Lean Canvas PDF template
We’ve prepared a blank Lean Canvas PDF template for you. It will fit within A4 format if you print it out – so that you’re not tempted to go into elaborate details.
When do you use Lean Canvas?
In the product development process, the Lean Canvas is most valuable during the early stages, specifically:
- Ideation and concept development
- Problem-solution fit validation
- Product-market fit exploration
While primarily beneficial in the early stages, Lean Canvas can and should be used iteratively throughout the development process.
As you gather feedback and gain new insights, you can revisit your Lean Canvas and update it to reflect the evolving product and market landscape. This allows for continuous improvement and ensures your product remains relevant to your target audience. Learn why continuous product discovery is so important for building lasting products.
Remember, the Lean Canvas itself is not a rigid process. It’s a flexible framework that adapts to your specific needs and allows you to iterate and refine your product and business model continuously.
I usually start working with Lean Canvas by filling in the “Problem” and “Customer Segments” blocks. The next step is defining “Key Metrics” by answering the question: “How will we measure that this particular problem will be solved for our clients by the solution we want to create?” It very often drives me to different solution ideas than I had at the beginning. |
Why is Lean Canvas beneficial for startups?
As mentioned previously Lean canvas is a business model canvas but more entrepreneur-focused and designed for startups at the beginning stage. Some of the main benefits of it are:
- The lean product canvas forces startups to distill their product vision into a simple, concise document.
- It helps founders focus on the most important aspects of their product and avoid getting bogged down in unnecessary details.
- The lean product canvas can be used as a tool to help validate or invalidate a startup’s business model.
- It is a valuable resource for communicating with potential investors and customers.
- It’s easy and quick to put together and allows everyone to be on the same page.
Taking all of this into account, using Lean Canvas instead of a traditional business plan is the best route for startup founders who want to challenge their ideas before launching an MVP. Additionally, it is easy to change and update as your ideas progress.
How do you use Lean Canvas?
Lean Canvas is made up of 9 blocks that guide you through the necessary areas that need to be considered, starting from the customers all the way to the cost structure. As you move forward you fill in the blocks with information that will help you gain clarity and shape your business idea.
To fill in your Lean Canvas you can use:
- A printed pdf lean canvas template,
- A whiteboard and sticky notes, or
- Other tools, such as Miro.
The Lean Canvas template takes around 20 minutes to complete and should be done in one sitting with your team. You can always come back to it to update your business model or if you need to brainstorm ideas for a new feature in the future.
There are no strict rules regarding the order that the blocks should be filled in but in this article, we will present the common method of filling in the Lean Canvas template.

1. Problem
In this part of the Lean Canvas, we focus on the problem that we are going to solve. Without a problem, there is no product or service to offer. Put yourself in the customer’s shoes and understand the pain points and challenges they are dealing with. Make a list of one to three problems that you want to provide a solution for. Try not to clutter this space with too many ideas, it’s good to start small and as you make progress in your startup journey you can make room for new issues to address.
2. Customer Segments
It’s extremely important to get to know the group of users you are targeting. We can use the Lean Canvas model to explore and define potential clients that are struggling with the problem defined in the previous step.
Try to be as specific as possible in defining your target customer as this will help you later with marketing. A common mistake that you should avoid is defining your audience too broadly. Remember that you can’t fulfill the needs of everyone. However, if you think that your product could be solving different problems for several customer segments it’s beneficial to create a separate Lean Canvas for every customer segment. It is also possible that it will be solving the same problems differently for different user groups.
Getting to know your target market is beneficial not only in the beginning stages of your product but it’s something you will have to consider as you move forward with it. A good understanding of your audience will help you improve your product and build strong customer relationships. Check out our previous articles to learn more about how to conduct market research and how to do desk research to get to know your users.
3. Key Metrics
How will you know if you’ve solved the problem?
To make sure that your startup is heading in the right direction you will have to pay attention to some key metrics. They will help you keep a close eye on the performance of your business.
Key metrics can range from the number of social media mentions to actual purchases of your product. You can monitor different key activities to learn how your potential clients are using your product and what their impressions are of it.
4. Solution
This part of the Lean Canvas focuses on describing the solution your product will offer. How will your product answer the pain points of your potential customers? What solution are you going to offer them? Brainstorm the different possibilities of solving the problem and refine your proposed solutions through testing. It’s a good idea to actually get out there and interview your customer segments to find out what they truly need.
Remember that nothing in the Lean Canvas process is set in stone – it’s okay not to have the perfect solution straight away. But if you use the Lean Canvas method it will help you with getting started. Testing and redefining are all features of a lean startup, so be prepared for making adjustments to your plan.
5. Unique Value Proposition
What is so unique about your product?
The next step is filling in the section that sits in the center of the Lean Canvas template, and that is the Unique Value Proposition. The UVP is an important element to consider when structuring your business plan. It is your promise to the users and the reason that they should choose your product over the one that is offered by the competition. In other words – what makes your solution unique?
To define your unique value proposition it is a good idea to do some research and check how others are solving the same problem. Are there any existing alternatives to your product? How will your product be different and how will it benefit your users? You need to make sure that you stand out and that people have a reason to choose your product.
6. Unfair advantage
What do you have that nobody else has?
This part of the Lean Canvas model for your product might be a bit tricky to answer and you might need to revisit it as you make progress. You can think of the unfair advantage as something that your competitors can’t copy or buy. It’s what makes your business stand out from the crowd. What competitive advantage do you have? Is there anything that you have that no one else could have (or at least it will not be easy for them to have)? To define this it will come in handy to have a clear image of your competitors and their advantages. Our blog post about competitor analysis will help you out with this and provide some useful tips.
Not every product needs to have an unfair advantage from the very beginning. Sometimes fast pace of development, quick hypothesis validation cycle, scalable growth, conquering the market fast, etc. are good enough competitive advantages to start with when filling in the Lean Canvas. Over time you can create an unfair advantage that will become more apparent.
7. Channels
How will you reach your customers?
Since we now have an idea of what problems we are going to solve, who has them, and how we intend to solve them the next step is to define how we are going to reach our prospects with our message.
The next segment of the Lean Canvas is focused on the channels you are going to use. Channels are the advertising and marketing methods that will use to deliver your value proposition. They include both digital marketing and more traditional channels, like radio or TV.
Here, we not only define our marketing and advertising channels but also collect basic information about our customers’ acquisition costs. We will use this data to help formulate our growth strategy.
8. Revenue streams
How are you going to make money?
At the end of the day, your product should generate some revenue. This part of the Lean Canvas Model is the place to describe how will it be generated. Where will you receive money from? How are you going to price your products or services? What is your product’s pricing model? These questions need to be answered before you launch your minimum viable product. The aim of every startup is to make a profit so make sure that there are ways you can monetize the solution you’re providing.
Ideally, you want your income to be bigger than the costs. How you price your product will depend on many factors, however, at this stage you should come up with a rough estimation of how much you can earn from your product.
9. Cost Structure
How much will it all cost?
Last but not least, now that we have more information about our product in place we can start estimating the cost of creating it. Therefore the last part of the Lean Canvas is related to the costs. Make sure to include all of the operational costs of your business in your Lean Canvas model. This could include expenses related to:
- product development
- tcost of customer acquisition
- market research
- marketing ads
- staff and labor costs
Lean Canvas is a great tool for helping you out with getting started and will increase the speed of the estimation process. However, in the long run, you will have to come back to your Lean Canvas and update it as the cost structure will change over time.
What are some common pitfalls when filling Lean Canvas?
We’ve explained how to approach each of the Lean Canvas sections but there are a few pitfalls you need to be aware of before you do it on your own.
- Confirmation bias: Don’t just confirm your own ideas, be open to feedback and adapt based on real data.
- Broad audience: Define a specific customer segment with clear needs, not a generic “everyone” group.
- Vague value proposition: Clearly state how your product benefits your target audience. No generic statements!
- Underestimating competition: Don’t neglect your unfair advantage – what makes you stand out? The more saturated the market, the more important this section becomes.
- Ignoring financials: Outline basic cost and revenue assumptions, even if not fully fleshed out.
- Solo act: Collaborate with others – team members, customers, advisors – for diverse perspectives.
- Static document: : Remember, the Lean Canvas is meant to be a living document that evolves. Update your Lean Canvas as you learn more about the market and your product.
- Features over value: Don’t fall into the trap of listing features without clearly articulating how each feature translates into actual value (=benefits) for your target customers.
- Missing channels: Plan how you’ll reach your target audience through specific channels.
- Skipping validation: The Lean Canvas doesn’t replace the need for market research and user testing. Use the Lean Canvas to form testable hypotheses, then gather data to validate or invalidate them.
It’s really, really important that whatever you put into your Lean Canvas is grounded in reality. Check this insight by Michał, one of our Senior Product Managers:
How to use Lean Canvas to test assumptions?
Above, we advised you not to skip validation… and now we will tell you how to do it step by step. Here’s how you can use Lean Canvas to test assumptions.
Here’s how you can use Lean Canvas to test assumptions:
1. Identify your key assumptions:
- Analyze each block of the Lean Canvas and identify underlying assumptions.
- Focus on the most critical and riskiest assumptions, as these have the biggest impact on your business model’s success.
2. Formulate hypotheses:
- For each identified assumption, formulate a clear and testable hypothesis. This states what you believe to be true about the assumption.
3. Define metrics and success criteria:
- Determine how you will measure the validity of your hypothesis. Choose relevant metrics based on the nature of the assumption, e.g. conversion rates.
- Set clear success criteria for each metric. What would make your test a success?
4. Conduct experiments:
- Design and conduct simple and low-cost experiments to gather data on your hypotheses. This could involve user interviews, surveys, landing pages, or minimum viable product (MVP) testing. There are various types of product launches and testing opportunities. so choose the one that fits your current product stage best.
5. Analyze results and iterate:
- Analyze the data collected through your experiments. Compare it to the success criteria you defined for each hypothesis.
- Based on the results, validate or invalidate your assumptions. If an assumption is invalidated, re-evaluate your business model and potentially pivot your approach.
- Update your Lean Canvas to reflect the new information and learnings gained from the test.
Lean Canvas. Conclusions
A key factor in the Lean Methodology is the elimination of waste.
The downside of traditional business plans is that they require a long and complicated process and won’t help you in the ideation stage. And a conventional business model canvas might not be ideal for companies that are just starting out.
As a startup, you need a faster way of getting your ideas down by using a lean business model canvas.
Lean Canvas + Product Discovery Workshop
If you have any doubts regarding business models or Lean Canvas you can count on the help of our experts.
Simply book a tailored Product Discovery Workshop session, and we’ll help you validate your business ideas through Lean Canvas and other product tools.











