NFT minting: Lazy minting vs. Regular minting [EXPLAINED]
If you’re building a business around NFTs — whether you’re launching a marketplace, gaming platform, or digital art collection — one of the first decisions you’ll face is how to mint your tokens. Should you mint every NFT upfront, or only when someone buys it?
This article breaks down Lazy Minting and Regular Minting, the two most common NFT strategies, and explains the trade-offs, ideal use cases, and technical underpinnings like ERC-721 and ERC-1155 smart contracts. Whether you’re optimizing for cost, user experience, or scalability, this guide will help you choose the right minting approach for your business.
Lazy Minting
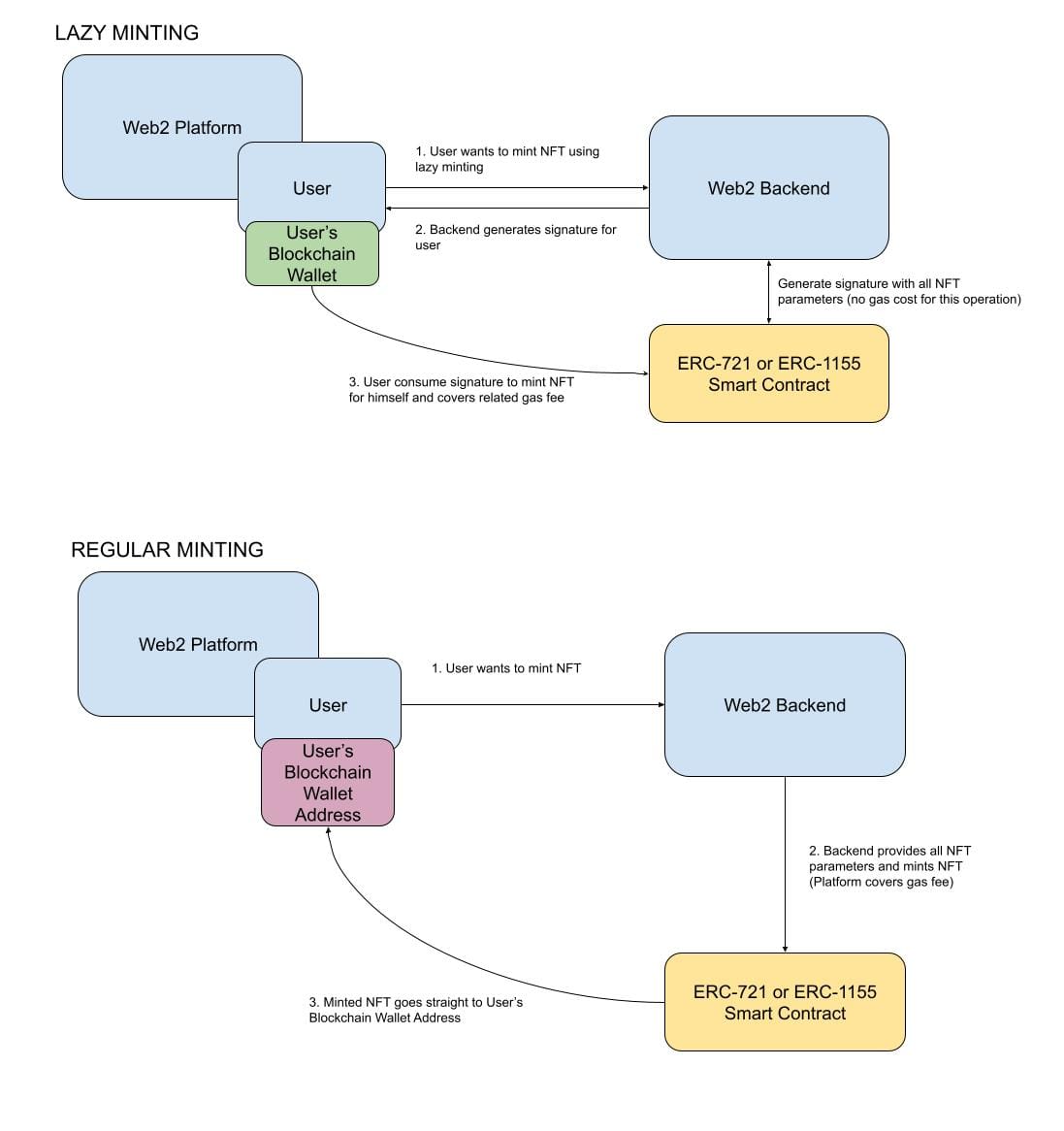
Lazy Minting allows users to create NFTs without upfront gas costs. Instead, NFTs are minted only when they are needed (e.g., purchased or transferred).
Business Pros & Cons of Lazy Minting:
✅ Pros:
- Lower Operational Costs: The platform avoids covering minting fees, reducing financial overhead.
- Easier User Onboarding: Users don’t need to pay gas fees upfront, removing friction from NFT adoption.
- Higher Conversion Rates: Users are more likely to create NFTs since there’s no initial cost, leading to a larger inventory.
- Efficient Inventory Management: Only NFTs that generate demand are minted, avoiding unnecessary blockchain congestion.
- Revenue Flexibility: The platform can introduce dynamic pricing models, charging fees only upon successful NFT sales.
❌ Cons:
- Delayed Revenue Capture: Since NFTs are only minted when purchased, businesses might experience inconsistent revenue streams.
- User Education Required: Users must understand how to sign transactions and complete the final minting step.
- Risk of Unsold Inventory: If an NFT isn’t minted immediately, its relevance may decrease before it’s ever placed on-chain.
- Potential Marketplace Liquidity Issues: Buyers may hesitate to purchase NFTs that are not immediately visible on-chain.
- Reliance on Web2 Backend Security: Signatures for minting are stored off-chain, posing a security risk if compromised.
Ideal Use Cases of Lazy Minting for Businesses
- NFT Marketplaces: Reduces platform costs and encourages more creators to participate.
- Gaming Platforms: Allows game assets to exist off-chain until needed, reducing blockchain congestion.
- Collectibles & Digital Art: Enables artists to create and showcase NFTs without upfront blockchain fees.
- Tokenized Ticketing: Tickets are only minted when sold, reducing operational costs.
Regular Minting
Regular Minting immediately creates NFTs on-chain, ensuring their authenticity and ownership from the start. The platform typically covers gas fees for a smoother user experience.
Business Pros & Cons of Regular Minting
✅ Pros:
- Guaranteed Authenticity & Ownership: NFTs are verifiable on the blockchain from the moment they are created.
- Instant Marketability: NFTs can be bought, sold, or transferred immediately, improving marketplace liquidity.
- Stronger Brand Trust: Buyers feel more secure when purchasing already-minted NFTs.
- Simpler User Experience: No extra steps are needed from the user, making adoption easier.
- Revenue Capture at Minting Stage: Businesses can charge fees or embed royalties into smart contracts upon minting.
❌ Cons:
- Higher Operational Costs: The platform must pay gas fees upfront, which can be expensive at scale.
- Blockchain Congestion Risks: Large-scale minting could lead to higher gas fees and network slowdowns.
- Reduced Scalability: If minting costs are too high, businesses might struggle to support a high volume of NFTs.
- Rigid Inventory Management: Once an NFT is minted, it cannot be easily modified or removed from the blockchain.
- Risk of Unused Assets: If an NFT does not sell, the platform incurs unnecessary blockchain storage costs.
Ideal Use Cases of Regular Minting for Businesses
- Luxury & Premium NFTs: Guarantees on-chain provenance for high-value digital assets.
- Limited Edition Drops: Ensures exclusivity by minting NFTs before a sale.
- Fan Engagement & Memberships: Businesses can issue on-chain loyalty rewards that users can immediately claim.
- Corporate NFT Campaigns: Ensures NFTs remain immutable and verifiable for long-term brand engagement.
Lazy Minting vs. Regular Minting: Comparison
| Factor | Lazy Minting | Regular Minting |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Costs | No gas fees initially (users pay upon minting) | Business pays gas fees upfront |
| Revenue Strategy | Fees earned at point of sale/minting | Fees earned at minting, with potential resale royalties |
| User Experience | Requires extra step to finalize minting | Seamless, instant ownership upon minting |
| Scalability | More scalable, less blockchain congestion | Limited by blockchain transaction fees |
| Inventory Risks | Only successful NFTs are minted, reducing waste | Business incurs costs for unsold NFTs |
| Liquidity & Marketability | May cause delays in secondary markets as NFT will be tradeable at the moment of mint by user | NFTs are immediately tradeable |
| Security Risks | Web2 backend must securely manage minting signatures | Fully on-chain, reducing backend risks |
| NFT Control | NFTs are fully under control of the user when minted. It is possible to create a custom NFT smart contract which can implement extra business logic. Downside of this approach could be potential project reputation loss due to interference in decentralized solutions like NFTs. | |
Diagrams showing the process differences between lazy minting and regular minting
Understanding ERC-721 & ERC-1155 Smart Contracts
NFT minting relies on Ethereum-based smart contracts, mainly ERC-721 and ERC-1155, which determine how NFTs are structured, owned, and transferred.
What is ERC-721?
ERC-721 is the first standard for non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on Ethereum, ensuring each token is unique and cannot be replaced with another. Every ERC-721 token has a distinct ID, metadata, and ownership.
What is ERC-1155?
ERC-1155 is a multi-token standard, allowing the creation of both fungible and non-fungible tokens within the same contract. This reduces blockchain congestion and transaction costs by enabling batch transfers.
ERC-721 vs ERC-1155: Comparison
|
Conslusions
If you’re a marketplace, game developer, or launching digital collectibles, lazy minting gives you scale and flexibility without frontloading costs. But if you’re creating premium NFTs, fan memberships, or brand collectibles, regular minting offers reliability, trust, and instant value.
Ultimately, the best approach depends on:
Your business model
Your audience’s expectations
Your budget for blockchain transactions
As the NFT ecosystem matures, hybrid models (e.g., pre-minting some, lazy-minting the rest) may offer the best of both worlds. The important part is understanding the implications — both technical and strategic — so you can mint smarter.
Also check: Is it possible to have anonymous transactions on public blockchain?
Need help with lazy or regular minting? We can help – check our blockchain portfolio.