How to automate your back office (with & without AI)?
The main goal of automation is to minimize the need for human involvement in a task, and there’s quite a lot of room for it, especially in the back-office departments of many companies: HR, finance, customer service, supply chain management & IT help desk.
This guide will navigate these complexities, 1. helping you understand back office automation, and 2. explaining how to implement it in your organization using AI.
AUTOMATE BACK-OFFICE WITH AI
What is back-office automation?
Back office automation is using technology to replace manual tasks and processes in a business’s administrative and operational departments. In our case, the technology will be artificial intelligence (AI).
Why AI matters for back-office operations
Back-office work is often time-consuming and repetitive, but it’s essential for keeping the business running – and AI can make it even simpler.
Here’s why AI is a game-changer:
- Saves time & reduces costs + improves accuracy + boosts productivity – Our AI accounting workflow automation helped our finance specialist, Martyna, save 2 hours daily (!). Thanks to this, she could focus on higher-value work and not worry about potential typos anymore.
- Enhances decision-making + scales easily – Our AI-powered recruitment workflow gathers information about potential candidates from their LinkedIn and Github profiles, then summarizes it and puts it on a range from 0 to 100. It saves our recruiters a huge amount of time. What’s more, it doesn’t matter if there are 10 or 1000 job entries – the workflow will analyze all of them in a fraction of a human recruiter’s time.
What to automate?
According to Zapier, SMBs most commonly automate the following back-office tasks:
- Manual data entry (38%)
- Lead management (30%)
- Document creation and organization (32%)
- Managing inventory and distribution (27%)
As you can see, these are very general types of tasks. As such, their automation can be applied across various back-office processes, for example:
- Invoice processing,
- Recruitment & onboatrding,
- Helpdesk ticketing,
- Contract review,
- Inventory tracking,
- Etc.
General AI-powered back-office workflow
Many back-office processes generally follow these four key phases, and AI can be applied at each step:
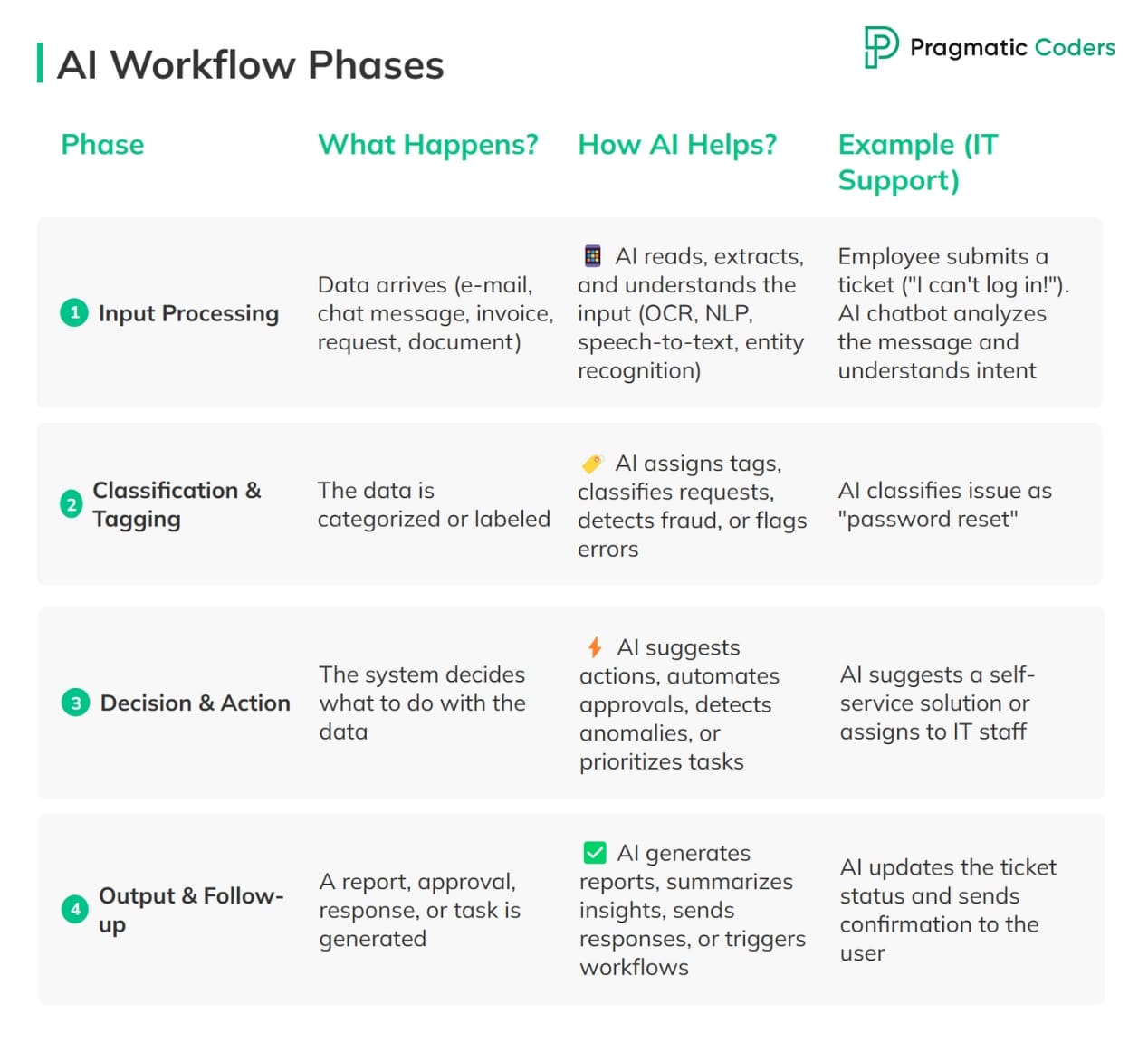
When to use AI back-office automation (and when not)
AI-powered automation can transform back-office operations, but it’s important to apply AI only where it adds real value. The key is to find the simplest, most effective solution, rather than overcomplicating processes with unnecessary AI tools.
✅ When to use AI for back-office automation
Use AI when it significantly improves efficiency, reduces errors, or enhances decision-making. The best applications involve:
- High-volume, repetitive tasks: AI is ideal for automating tasks that involve processing large amounts of structured or semi-structured data. Examples: invoice processing (AI reads, extracts, and categorizes invoices) or customer email triaging (AI routes support requests).
- Tasks that require pattern recognition & prediction: AI can identify trends, anomalies, or predict outcomes better than humans. Examples include fraud detection, cash flow forecasting, or HR attrition analysis.
- Workflows that benefit from intelligent decision-making: AI enhances processes where rules alone aren’t enough and decision-making requires context awareness. For instance, AI could be used to review contracts highlight risks based on legal databases).
- When cost & speed gains justify the AI overhead – when the tradeoff between latency, cost, and accuracy is worth it.
❌ When not to use AI for back-office automation
Not every workflow needs AI—sometimes simpler rule-based automation or human oversight is the better choice.
- When rule-based automation is enough: If a task follows clear, structured rules, traditional automation (like RPA) is often cheaper and faster than AI. You don’t need AI for auto-replay emails or simple approval workflows (if invoice < $5000 → auto-approve).
- When errors have high stakes & AI can’t be trusted fully: AI is not 100% reliable and should not replace human oversight in critical workflows.
- When AI complexity outweighs the benefits: If AI increases costs, latency, or maintenance effort without a clear benefit, it’s not worth implementing. Building an AI agent for simple data entry wouldn’t make much sense, since RPA is faster & cheaper. Similarly, manually processing a few invoices per month is fine, and not worth the AI implementation cost.
- When AI needs more data than you have: AI models rely on large datasets to be effective. If your data is inconsistent or limited, AI may not perform well. Examples: AI-powered HR analytics when a company only has 10 employees or AI-based financial forecasting with incomplete transaction history.
The above guidelines lead us further to 2 conclusions:
Automatable tasks share 9 characteristics
A task is worth being automated with AI if it has at least a few of the following characteristics:
- Repetitive – The task follows the same steps every time.
- Rule-based – It has clear, predefined rules with little need for human judgment.
- High-volume – The task occurs frequently or at scale.
- Low exception rate – Rarely requires special handling or case-by-case decisions.
- Data-intensive – Involves processing, transferring, or managing large amounts of data.
- Structured or semi-structured data – Input data follows a consistent, predictable format.
- Time-consuming – The task takes significant manual effort to complete.
- Requires accuracy & consistency – Mistakes can be costly, and automation improves precision.
- Cost-effective to automate – The efficiency and cost savings outweigh the investment in automation.
Sometimes it’s best to use AI sparingly or not at all
Take a look at the 3 AI-backed workflows we created.
The grayed-out areas are those where AI is NOT used; the four light rectangles – the bricks in the workflows that indeed use AI.
As you can see, we used AI sparingly, as single elements in greater processes. We could push artificial intelligence into more chains in these workflows, but that could have been an unnecessary complexity that wouldn’t trade for meaningful efficiency gains.
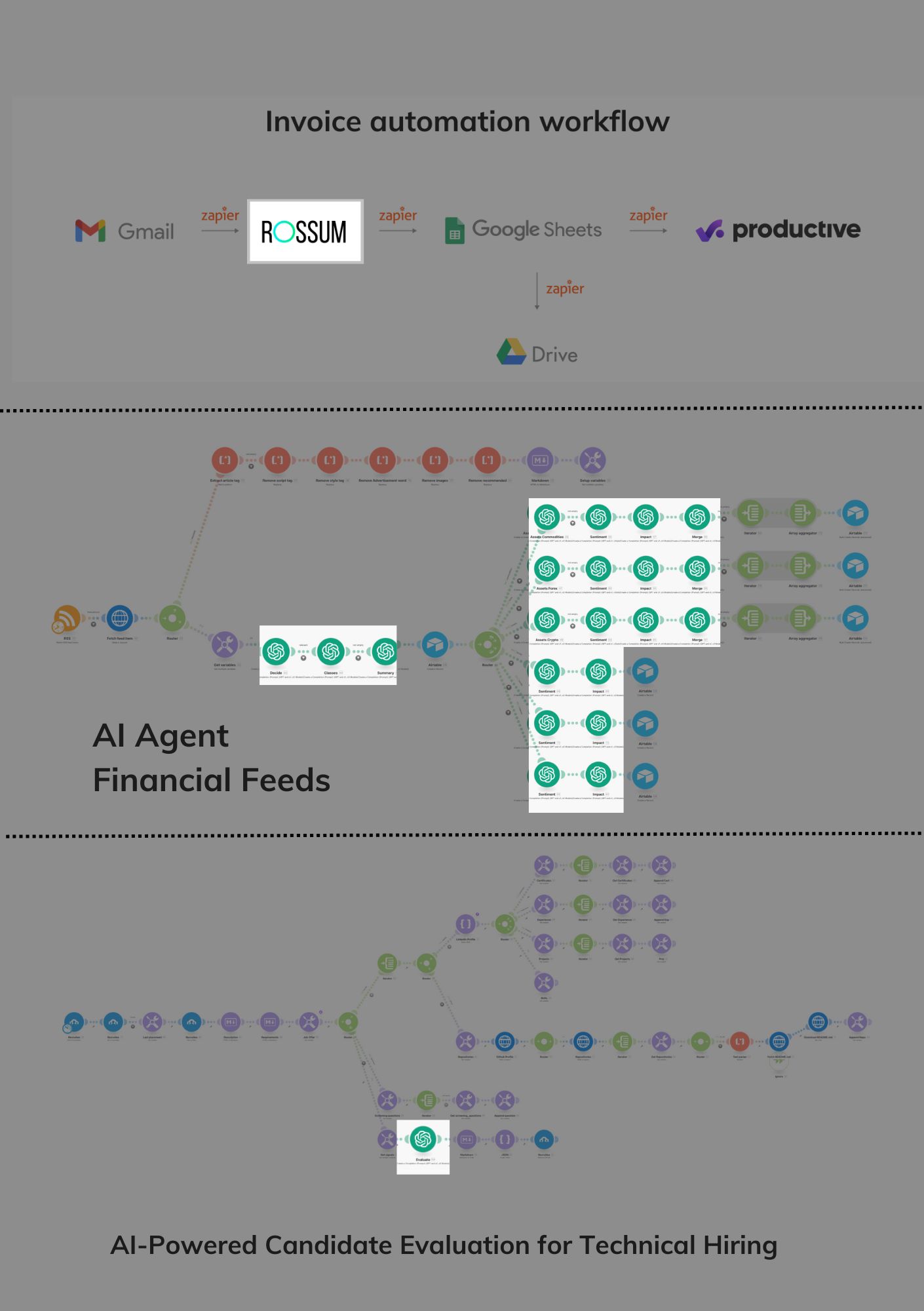
Back office automation examples
No hollow words. We’re praising back-office automation because we’re actually implementing it within Pragmatic Coders.
Below, I’ll shortly describe 3 use cases of how we automated the back-office tasks for our HR & finance departments. For an even more in-depth explanation, I encourage you to read the full case studies.
HR automation
Below, you’ll find 2 examples of automations the HR team at Pragmatic Coders uses. Here’s 6 more: How to automate your HR department
Training automation system for our HR department
Problem: Our HR department struggled with managing employee training as the company grew. Manual tasks were time-consuming and inefficient.
Challenge: Develop a training management system quickly and affordably.
Solution: We used a low-code platform (Adalo) to build an MVP with core features:
- Employees self-enroll in training;
- Instructors manage dates and attendance;
- The system integrates with calendars to send a notification for training updates and generates reports.
Outcome: In this simple case, using AI wasn’t even necessary. The long and time-consuming process of managing internal employee training is now history. All the work on an employee’s side ends when they click “Accept.” Since the meetings are automatically added to their Google Calendars, they don’t have to do it manually. And once they’ve attended a training session, they don’t even have to sign the attendance list.
HR training management software: Automate employee training
Discover how we helped our HR department streamline employee training by developing a custom automation system in less than 3 weeks.
Learn MoreAI-powered candidate evaluation for technical hiring
Problem: Screening technical candidates took too much time and effort.
Challenge: Automate early-stage candidate evaluation.
Solution: We built an AI tool that:
- Pulls data from LinkedIn, GitHub, and other sources.
- Analyzes skills, experience, and gaps.
- Integrates with Recruitee to generate reports automatically.
Outcome: Faster, objective, and data-driven candidate screening. Recruiters get instant insights with less manual work.

Automate recruitment: How to automate tech hiring with AI
We created an AI-powered workflow to automate tech candidate evaluation. It saves us time and ensures objective & data-driven hiring.
Learn MoreFinance automation
How to automate back-office finance tasks? Our AI & low-code accounting automation system
Problem: Martyna (our finance specialist) spent 2 hours daily on manual bookkeeping tasks: organizing financial data from different departments, manually entering invoice data into various systems, and moving files. She wanted to automate these tasks.
Solution:
- Implemented AI-powered OCR (Rossum) for data extraction from invoices;
- Used Zapier to automate data flow between systems (Gmail, Rossum, Google Sheets, Google Drive, Productive);
- Created formulas in Google Sheets for automatic categorization and organization.
Outcome: This is a great example of AI streamlining tasks and processes. This automation helps Martyna save 2 hours daily on repetitive tasks and helps us save costs, as the monthly cost of Rossum and Zapier combined is significantly lower than Martyna’s hourly wage. Finally, the data is automatically moved through each part of the workflow, which reduces the chance of typos and human error, and Martyna has more time for other activities.

Saving 2 hours daily: efficient AI & low-code accounting automation
We’ve helped our finance specialist get rid of daunting bookkeeping tasks and save her up to 2 hours every day with AI & low-code.
Learn More
Marketing SEO automation (backlink automation)
Problem
Our SEO agency offered a 12-month backlink warranty, but we had no system to track lost links among 5,489 total—over 200 of which were agency-built. Manual checking was unfeasible.
Monitor a subset of backlinks automatically—without coding expertise—to identify missing links eligible for warranty replacement.
Solution & results
I vibe-coded Apps Script code for a Google sheet where I store backlink reports from the agency. It’s enough to click a button, and the link analysis starts, and I get a clear list of missing links. Thanks to that, I identified 31 lost backlinks worth ~$10,600 in warranty value. Enabled ongoing, code-free monitoring—saving hours of manual work and empowering a non-technical marketer like me to solve a technical problem with AI.
Learn more here: How I Built a Backlink Monitoring Tool with AI (& No Coding Skills)
How to implement back-office automation that contains an AI component
What processes do you want to automate? What are your desired outcomes? Clearly define your objectives to guide your selection and implementation.
Then, start by identifying the most repetitive and time-consuming tasks in your back-office operations. Look for processes where AI can improve speed, accuracy, or decision-making. Check the tasks you were thinking about against the 9 characteristics mentioned above – it will help you decide whether a task is worth automating.
Next, choose AI tools that integrate easily with your existing software—whether it’s AI-powered OCR for invoice processing, chatbots for IT helpdesk requests, or machine learning models for predictive analytics.
- This part might be harder if you don’t have IT specialists on board. If that’s the case, check our AI agent development services – we will build a POC (Proof-Of-Concept) to check if your idea is tangible, and help you design the automation workflow in a way that’s both cost-effective and productive. ⬇️
AI agent development
Challenges in back-office automation
While AI-powered back-office automation offers many benefits, it also comes with its share of hurdles.
The major challenge is integrating AI within existing software and processes. Many businesses rely on legacy systems that don’t easily connect with modern AI tools. This often requires additional middleware, custom APIs, or even system upgrades, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Another challenge is data quality. AI models need clean, structured, and sufficient data to function effectively. If your back-office data is inconsistent, incomplete, or stored across multiple disconnected systems, AI may struggle to deliver accurate results. Companies often need to invest in data standardization before automation can work properly.
AI isn’t foolproof. Errors can still happen, and over-reliance on AI without human oversight can lead to costly mistakes.
Finally, data security. The way you set up AI in your back-office (and where you store it) affects how secure your data is.
How to overcome them
Process automating & AI development are challenges our clients face on a daily basis.
To help them focus on their core business activities (instead of trying to come up with an automation solution from scratch) we’ve come up with our AI agents development services that address all the hurdles named above:
| ❌ You have existing back-office software and process, and you don’t want to turn them upside down | ✅ We find the best way to add AI to your existing workflows and software without a costly overhaul |
| ❌ You have inconsistent data scattered all over the place | ✅ We help you extract, clean, and secure the right data for effective automation |
| ❌ You’re afraid something unpredictable will happen to your back-office when you add AI | ✅ In our subscription model, you get 24/7 support |
| ❌ You’re afraid of what happens to your data | ✅ We have 3 collaboration models that differ in where the data is stored ⬇️ |
- AI Agent as a Service – If you don’t have an in-house tech team, you can use a fully managed AI service. We take care of infrastructure, security, and maintenance, so you don’t have to worry about it.
- Self-Managed AI Agent – If your company has strict privacy rules, you can host AI on your own servers or a private cloud. This gives you full control over data security and compliance, but you’ll need a strong IT team to manage it.
- Pay-as-You-Go AI Agent – If you want a low-cost, flexible AI setup, you can use cloud-based AI tools that charge based on usage. This is great for quick automation, but you must ensure the cloud provider follows security standards.
You can learn more here:
AI agent development
The best choice depends on your company’s security needs, technical skills, and budget. If you’re not sure which option is right for you, don’t hesitate to contact us.
Conclusion
Automation is quickly changing back-office processes. We can see more and more companies implementing or have implemented automation already.
Need help implementing custom automation into your business operations? Or maybe you want to build an automation app?
Just hop on a call with our team.
Together, we’ll find the best solution to match your needs, be it through AI integration, custom AI development, low-code development, or any other way.








