How to Engage Stakeholders Effectively: Key Strategies

Engaging stakeholders is crucial for any successful project or initiative. Without their support, even the best-laid plans can falter. By understanding their needs, fostering open communication, and involving them throughout the process, you can build strong relationships that lead to positive outcomes and project success.
Key Points
|
Understanding Stakeholder Needs and Expectations
At the heart of effective stakeholder engagement is a deep understanding of their needs and expectations. By recognizing what stakeholders value, you can align project goals with their interests. This alignment fosters a collaborative environment built on trust.
Stakeholders can include internal team members, management, clients, suppliers, investors, or community members. Each group may have different priorities and concerns. For example, investors might focus on return on investment, while community members may care more about your product staying true to its initial vision.
Building Trust Through Alignment
To build trust:
- Conduct Stakeholder Analysis: Identify who your stakeholders are, their interests, and how the project might affect them. Use methods like surveys, interviews, and stakeholder mapping. Adding UX research can be a great way to gain deeper insights into user needs and behaviors, ensuring the project aligns with stakeholder expectations.
- Engage Early and Often: Involve stakeholders from the project’s start. This ensures their needs are considered and reduces resistance later on.
- Demonstrate Transparency: Openly share information about project goals, progress, and challenges. Being transparent fosters credibility and confidence in your project’s leadership.
- Sometimes trust has already been damaged by missed deadlines, unclear communication, or earlier vendor failures. If you want to explore how to move stakeholders from a state of crisis toward clarity and partnership, take a look at our guide on managing stakeholders during a project rescue.
Example: A construction company planning a new development might hold community meetings to hear residents’ concerns about noise and traffic. By addressing these early, they could tweak their plans to reduce disruptions. This approach builds trust and shows they value community input.
Defining Your Key Stakeholders
Not all stakeholders have the same level of influence or interest in a project. Prioritizing key stakeholders helps you focus resources and engagement efforts where they’ll have the greatest impact.
Steps to Effective Stakeholder Identification
Listing Potential Stakeholders
Start by brainstorming all individuals and groups who may be affected by or have an interest in the project. This list might include employees, customers, influencers, suppliers, investors, regulators, community groups, and others. Casting a wide net ensures no critical voices are overlooked and gives you a clear picture of the stakeholder landscape.
Assessing Influence and Interest
Evaluate each stakeholder based on decision-making power, level of investment, or degree of impact. Determine who can influence project outcomes and who will be most affected by its success or failure. This helps identify key players whose support is crucial and those who may pose challenges.
Creating a Stakeholder Map
Use visual tools like an Influence/Interest Matrix to categorize stakeholders into groups like ‘Key Players,’ ‘Keep Satisfied,’ ‘Keep Informed,’ and ‘Minimal Effort.’ This mapping lets you develop targeted engagement strategies for each category, ensuring your efforts are efficient and effective.
Example: In a software project, mapping might show that regulators have high influence but mixed interest levels. Knowing this helps the team focus on compliance and allocate resources where they’re needed most.
Mapping Stakeholder Influence and Relationships
Understanding the relationships and dynamics between different stakeholders helps you anticipate potential alliances or conflicts. For example, an influencer can easily shape their community’s perception of an issue. Recognizing this influence allows you to adjust your engagement strategy to build support and address potential challenges effectively.
Techniques for Stakeholder Mapping
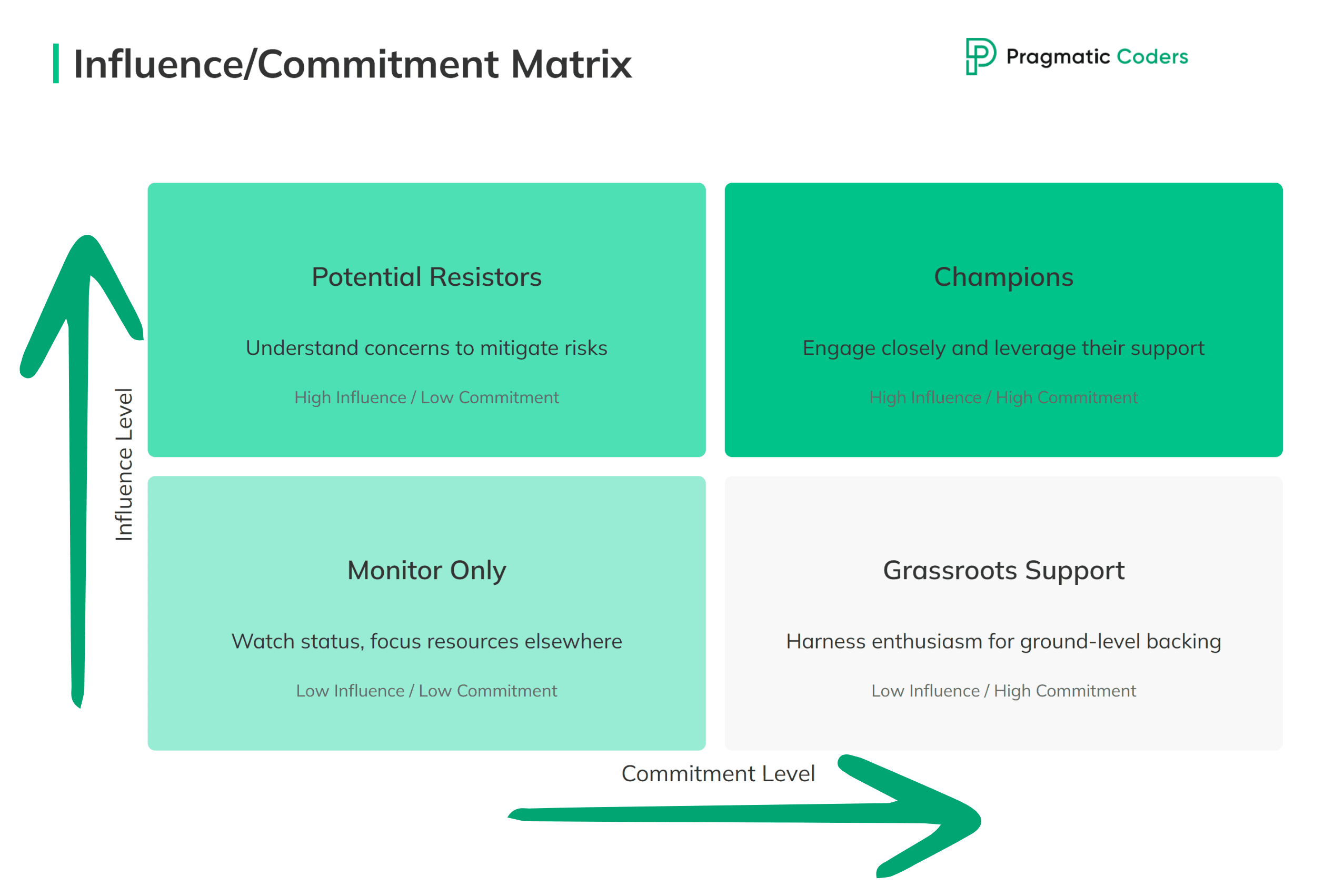
Influence/Commitment Matrix
This matrix plots stakeholders based on their influence over the project and their commitment to its success. Positioning stakeholders within this framework helps identify who is likely to support or hinder your efforts.
- High Influence, High Commitment: Your champions. Engage them closely and leverage their support.
- High Influence, Low Commitment: They may resist the project. Understanding their concerns is key to mitigating risks.
- Low Influence, High Commitment: Their enthusiasm can be harnessed for grassroots support.
- Low Influence, Low Commitment: Monitor them but allocate resources elsewhere unless their status changes.
Network Analysis
Examining how stakeholders are connected can uncover influential individuals who can champion the project. Network analysis helps identify key influencers, communication patterns, and potential information bottlenecks.
- Identifying Central Figures: Stakeholders who act as hubs can amplify your messages.
- Understanding Subgroups: Recognize clusters with shared interests or concerns.
- Leveraging Relationships: Build strategic partnerships based on existing connections.
Political Environment Assessment
Consider organizational politics that might affect stakeholder behavior. Analyze power structures, informal alliances, and historical relationships that could influence project dynamics.
- Assessing Power Dynamics: Identify who holds formal and informal power.
- Understanding Motivations: Recognize the underlying interests driving stakeholder actions.
- Navigating Sensitive Areas: Develop strategies to address or avoid potential political pitfalls.
Example: An organization introducing agile practices might find that a veteran employee, who has trained many younger colleagues, holds significant informal power. Engaging this individual positively can help build support for the change and encourage broader acceptance across the team.
Stakeholder Communication and Engagement Plan
Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful stakeholder engagement. Tailoring your messages to address specific concerns and preferences enhances understanding, builds trust, and fosters cooperation.
Developing a Communication Plan
Defining Objectives
Clearly outline what you aim to achieve with your communication efforts. Objectives may include informing stakeholders about developments, addressing concerns, soliciting feedback, or encouraging participation.
Segmenting Stakeholders
Group stakeholders based on their communication needs, preferences, and influence levels. This allows for personalized messaging, ensuring information is relevant and engaging.
Selecting Communication Channels
Choose the most effective methods for reaching each group:
- Emails and Newsletters: For regular updates to a broad audience.
- Face-to-Face Meetings: For high-influence stakeholders needing personalized engagement.
- Social Media and Websites: For public outreach and transparency.
- Reports and Presentations: For detailed information sharing with technical or managerial audiences.
Establishing Communication Frequency
Determine how often you’ll communicate with each group. Regular, predictable updates help maintain engagement and trust without overwhelming recipients.
Tailoring Messages for Impact
Using Clear and Accessible Language
Avoid jargon and technical terms unless appropriate. Clear, concise language ensures your message is understood by all stakeholders.
Addressing Specific Interests
Focus on how the project benefits or affects each stakeholder. Highlighting relevant aspects shows you value their concerns and fosters a stronger connection.
Providing Actionable Information
Empower stakeholders by including steps they can take or decisions they need to make. Clear calls to action facilitate participation and collaboration.
Example: When introducing agile to a company, use straightforward language and emphasize key benefits, such as quicker time-to-market and improved adaptability. Highlighting these advantages can help build organizational support and alignment.
How to Encourage Stakeholder Feedback and Participation
Active involvement from stakeholders leads to better outcomes and stronger commitment. Encouraging feedback and participation ensures diverse perspectives are considered, enhancing the project’s relevance and acceptance.
Methods to Encourage Engagement
Interactive Workshops
Organize sessions where stakeholders can contribute ideas and solutions collaboratively. Workshops promote open dialogue and creative problem-solving.
- Facilitated Discussions: Guided conversations that keep participants focused.
- Breakout Groups: Smaller teams for deeper exploration of topics.
- Hands-On Activities: Interactive exercises to make complex concepts accessible.
Feedback Mechanisms
Implement systems for continuous input, like suggestion boxes, surveys, or online forums. These provide convenient channels for stakeholders to express their thoughts and concerns.
- Anonymous Submissions: Encourage honest feedback without fear.
- Regular Surveys: Collect data on satisfaction and areas for improvement.
- Digital Platforms: Use apps or websites for real-time engagement.
Stakeholder Advisory Panels (for larger projects)
Establish committees or panels that offer ongoing advice and perspectives. These groups provide valuable insights and serve as liaisons between the project team and broader communities.
- Diverse Representation: Include members from different groups to capture a wide range of views.
- Clear Mandates: Define the panel’s purpose and responsibilities.
- Regular Meetings: Maintain momentum and continuous engagement.
Benefits of Active Stakeholder Participation
Improved Decision-Making
Getting input from a variety of stakeholders leads to better, more practical solutions. Different perspectives can highlight challenges or opportunities that might have been missed. This collaborative approach helps the team make decisions that are well-rounded and more likely to succeed.
Enhanced Commitment
When stakeholders are involved in the process, they feel more connected to the outcomes. This sense of ownership makes them more likely to support the project and less likely to push back. Engaged stakeholders can also help generate excitement and encourage others to get on board.
Early Identification of Issues
Engaging stakeholders early gives you a chance to spot problems before they grow. Addressing concerns right away saves time and keeps things moving smoothly. It also shows stakeholders that their input matters, which helps build trust and strengthens relationships.
Example: Involving employees in rolling out a new internal system can lead to a smoother transition. Their feedback might highlight usability issues or training needs that management overlooked.
Strategies for Conflict Resolution
When multiple stakeholders are involved, conflict isn’t a question of if—it’s a question of when. Different priorities, perspectives, and expectations can naturally lead to disagreements. However, conflict doesn’t have to derail your project. With the right strategies, you can turn challenges into opportunities for collaboration and innovation. Here are some of them:
Establishing Clear Protocols
Develop predefined processes for managing conflicts to ensure consistency and fairness. These might include steps for reporting issues, response timelines, and designated mediators.
- Conflict Resolution Policies: Document guidelines accessible to all stakeholders.
- Designated Contact Points: Assign individuals responsible for handling disputes.
- Transparent Procedures: Communicate steps involved so stakeholders know what to expect.
Promoting Open Dialogue
Encourage an environment where stakeholders feel comfortable expressing concerns. Open communication helps prevent misunderstandings and allows early detection of conflicts.
- Regular Meetings: Provide forums for discussion and feedback.
- Active Listening: Show genuine interest in viewpoints.
- Non-Judgmental Approach: Respectfully acknowledge all perspectives.
Focusing on Interests, Not Positions
By understanding the underlying interests behind stakeholder positions, you can find common ground and develop mutually beneficial solutions. This moves beyond entrenched stances to address real needs.
- Interest-Based Negotiation: Explore why stakeholders hold certain views.
- Collaborative Problem-Solving: Work together to generate options satisfying shared interests.
- Win-Win Solutions: Aim for outcomes where all parties feel their needs are met.
Example: In a community development project, conflicting opinions about land use might arise. For example, balancing economic growth with environmental preservation can lead to a compromise, like incorporating sustainable practices.

Engaging Stakeholders Through Storytelling
Storytelling is a great way to connect with stakeholders on a personal level. It makes your project’s purpose clear and its impact real. By sharing relatable stories and using visuals, you can build trust, spark interest, and keep people engaged.
Utilizing Personal Narratives
Share stories of individuals impacted by the project to humanize your efforts. Personal accounts create emotional connections and illustrate real-world significance.
- Testimonials: Feature experiences from beneficiaries or team members.
- First-Person Stories: Let stakeholders share their journeys in their own words.
- Relatable Characters: Highlight people your audience can identify with.
Developing Case Studies
Provide detailed examples of success and challenges overcome to offer insights and lessons learned. Case studies demonstrate effectiveness and inspire confidence.
- Problem-Solution Format: Outline obstacles faced and how they were addressed.
- Data-Driven Results: Include metrics to substantiate claims.
- Relevance: Choose cases that resonate with your audience’s interests.
Employing Visual Storytelling
Use videos, infographics, and images to convey messages compellingly. Visuals simplify complex information and capture attention more effectively than text alone.
- Short Films: Create engaging videos that tell a story succinctly.
- Infographics: Present data in an appealing and digestible format.
- Photography: Use images to evoke emotions and highlight key moments.
Example: A charity produces a video showing how donor contributions have transformed lives, motivating continued support.
How to Improve Stakeholder Engagement
Monitoring Engagement Levels
Regularly assess how stakeholders interact with the project to identify areas for improvement. Metrics might include participation rates, feedback quality, and response times.
- Analytics Tools: Track engagement metrics across platforms.
- Benchmarking: Compare current levels against past performance or industry standards.
- Trend Analysis: Observe patterns to anticipate future needs.
Gathering Feedback on Engagement Methods
Ask stakeholders about the effectiveness of your communication and participation strategies. Their insights can reveal strengths to build upon and weaknesses to address.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Collect structured feedback efficiently.
- Focus Groups: Engage in-depth discussions about experiences.
- One-on-One Interviews: Obtain detailed insights personally.
Staying Informed of Best Practices
Keep up with the latest trends and tools in stakeholder engagement to ensure your approaches remain relevant and effective.
- Professional Development: Attend workshops, webinars, and conferences.
- Industry Publications: Read articles, case studies, and reports.
- Networking: Connect with peers to share experiences.
Conclusion
Effective stakeholder engagement is multifaceted. It requires a strategic approach that considers the diverse needs and expectations of everyone involved. By investing time and resources into understanding stakeholders, tailoring communication, encouraging participation, resolving conflicts, celebrating achievements, leveraging technology, and continuously improving your practices, you can build strong relationships that are essential for project success.








