Essential guide to HIPAA-compliant software development

In the realm of healthcare software development, understanding the significance of HIPAA is paramount. For anyone venturing into the creation of medical software in the US, compliance with HIPAA is not a choice but a necessity.
In this article, we delve into the crucial aspects of achieving HIPAA-compliant software development.
What is HIPAA?
HIPAA, or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, is a federal law enacted in the United States in 1996.
Its primary purpose is to protect sensitive patient health information, ensure the privacy and security of individuals’ medical records and personal health information (PHI), and prevent data breaches.
I’m developing a healthcare app. Do I need HIPAA compliance?
Whatever type of medical software you’re developing, if your healthcare app handles, stores, or transmits protected health information of US citizens, you need to comply with HIPAA requirements.
HIPAA regulations apply to “covered entities” (such as healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses) as well as their “business associates” (third-party entities that handle PHI on behalf of covered entities).
EXAMPLE
You’re the owner of a private health hospital in the US looking for healthcare software developers to help you build an app to manage your patient data. In this case, you’re the covered entity, and the outsourced software development team you’re working with will be your business associate. The app needs to be HIPAA-compliant.
What is Protected Health Information (PHI)?
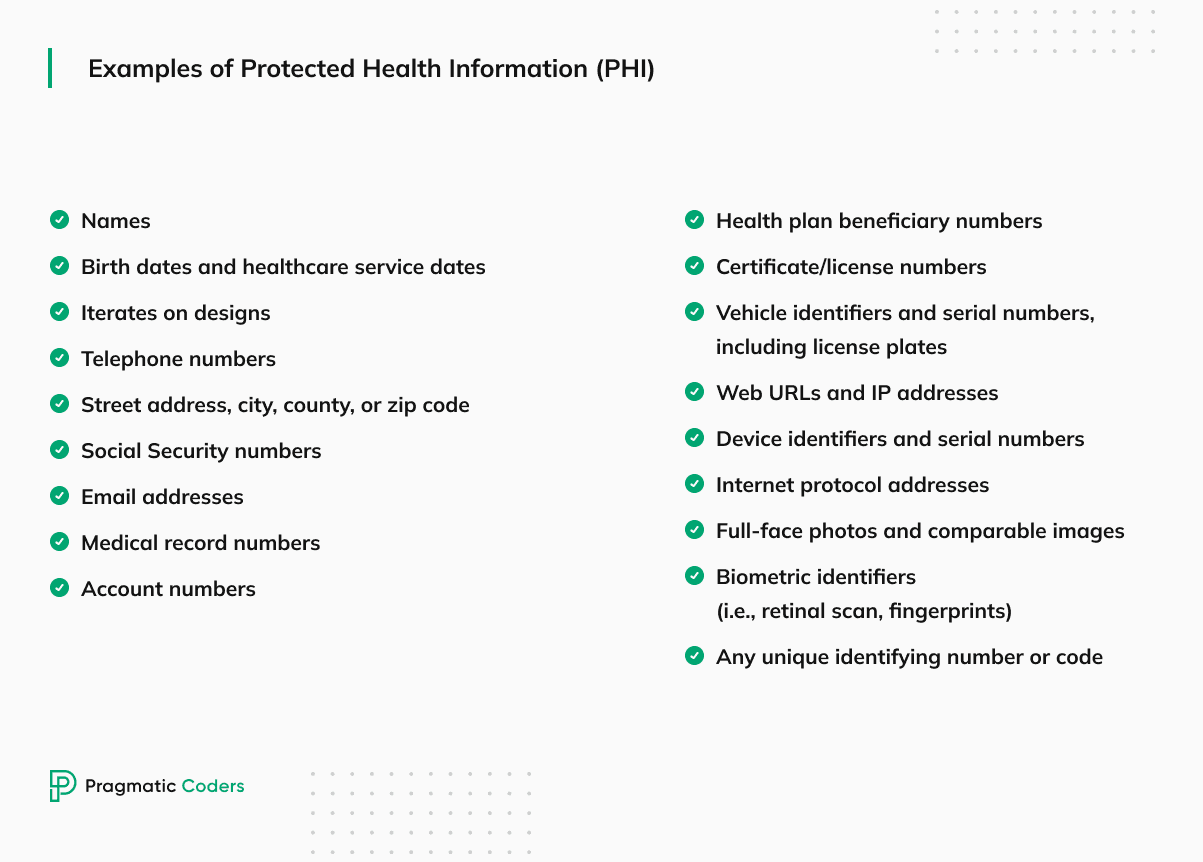
Protected Health Information (PHI) is any individually identifiable medical data created, received, transmitted, or maintained by a covered entity or a business associate.
Examples of Protected Health Information may include:
- Names, addresses, and other contact information combined with health-related data,
- Medical record numbers or patient identifiers,
- Dates of birth,
- Social Security numbers,
- Health insurance policy numbers,
- Medical images and diagnostic results,
- Any other information that could be used to identify an individual in the context of their health and healthcare services.
HIPAA-compliant software. Factors to determine if you need HIPAA
You will need HIPAA compliance if you deal with the Personal Health Information of people from the US – that’s all. Let’s inspect the topic from a few perspectives to better understand what it looks like.
HIPAA compliance applies in these cases:
- Handling of PHI: If your app collects, stores, processes, or transmits any form of PHI, such as medical records, treatment information, or health-related data.
- Business Associate Relationships: If your app collaborates with healthcare organizations, health plans, or other covered entities and you have access to PHI.
- Use Cases: If your app is involved in functions such as telemedicine, remote patient monitoring, electronic health record (EHR) integration, or any other activities related to healthcare that involve PHI.
- User Data: If your app collects personal health information from US users and is intended to be used for healthcare purposes.
When HIPAA regulations don’t apply to healthcare apps
As you already know, not all medical software must be HIPAA-compliant. Again, it all depends on the data usage, but here are a few examples of apps that are most likely unnecessary because they won’t deal with Personal Health Information.
- Wellness apps,
- Nutrition and diet apps,
- Healthcare education apps.
What are the HIPAA rules?
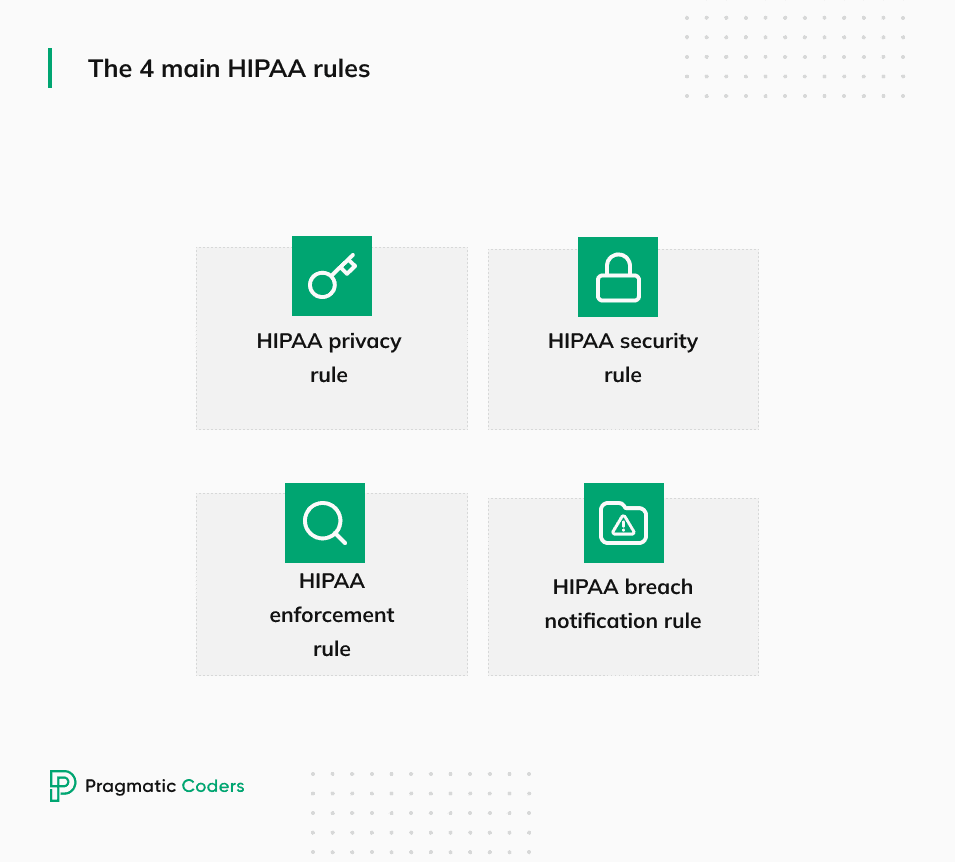
The HIPAA rules refer to regulations established under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. These rules are designed to safeguard sensitive health information and ensure proper handling within the healthcare industry.
The HIPAA privacy rule
The Privacy Rule outlines national standards for safeguarding individually identifiable health information.
It applies to three types of covered entities: health plans, healthcare clearinghouses, and healthcare providers conducting standard electronic healthcare transactions.
The HIPAA Privacy Rule protects individuals’ health information and limits its use and disclosure without authorization.
The HIPAA security rule
The HIPAA Security Rule establishes national standards for securing electronic protected health information (ePHI).
It ensures that your electronic health information is stored and transmitted securely to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches through administrative, physical, and technical safeguards.
Administrative safeguards
Administrative safeguards involve establishing a security management process within an organization. Examples of such measures include risk assessment, workforce training, assigning security responsibilities, and establishing security incident response plans.
Physical safeguards
These encompass the physical protection of electronic systems, equipment, and the facilities where electronic protected health information (ePHI) is stored or accessed. Examples include access controls, facility security plans, workstation policies, and device encryption.
Technical safeguards
Technical safeguards focus on the technology-based measures implemented to provide data security.
Examples of such measures are data backup of personal health records, data encryption, transmission security, access control, authentication mechanisms, and network security measures like firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
The HIPAA enforcement rule
The Enforcement Rule provides guidelines and standards for enforcing all the Administrative Simplification Rules, including the Privacy and Security Rules.
The rule outlines the procedures, investigations, and penalties for non-compliance with HIPAA regulations. It ensures that covered entities adhere to the privacy and security standards set forth by HIPAA.
The HIPAA breach notification rule
The Breach Notification Rule requires covered entities and business associates to notify affected individuals, the Secretary of Health & Human Services (HHS), and sometimes the media in case of a breach of unsecured protected health information.
This provision outlines the steps that must be taken in case of a breach. It helps ensure that affected individuals are informed promptly about potential risks to their health information.
The Omnibus rule
The Omnibus Rule was enacted by HHS to implement several provisions of the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act.
It strengthens the privacy and security protections for health information established under HIPAA and finalizes the Breach Notification Rule.
HIPAA FAQ
Is HIPAA compliance mandatory?
Yes, you need HIPPA compliance if your application handles PHI.
Why is HIPAA compliance important?
It’s vital to ensure HIPAA compliance for several reasons.
Increased security: Sticking to HIPAA guidelines naturally imposes improved security measures.
Enhanced reputation: Adhering to HIPAA regulations demonstrates a commitment to ethical and legal standards in healthcare. This enhances the reputation of covered entities, fostering patient and business partners’ confidence in the security and reliability of your product.
Avoiding legal and financial penalties: Non-compliance with HIPAA can lead to substantial fines and legal actions, potentially causing significant financial burdens on organizations.
Who will verify the compliance of my company with HIPAA regulations?
HHS is obligated to conduct regular audits on covered entities and business associates to ensure their adherence to the HIPAA Privacy, Security, and Breach Notification Rules regulations.
A HIPAA audit can be initiated due to a consumer complaint, a self-reported breach, or a random selection by the Office for Civil Rights (OCR).
Does HIPAA apply outside the US?
If a company outside the US manages or transfers the PHI of United States citizens, it is categorized as a business partner of a covered organization and, as a result, must adhere to the regulations outlined by HIPAA.
Does HIPAA apply to mobile apps?
HIPAA applies to mobile apps just like web apps. If the app handles protected health information and falls under HIPAA’s definition of covered entities or business associates, it must comply with HIPAA regulations, regardless of the platform it’s developed for.
How to choose the right software development company for building HIPAA-compliant software?
When embarking on the journey to develop HIPAA-compliant software, choosing the software development company is paramount.
Two key points should be considered to ensure a successful partnership:
1. Evaluate their MedTech experience
A crucial factor in selecting a software development company is their experience in the medical technology (MedTech) sector.
MedTech expertise indicates familiarity with healthcare software’s unique challenges and intricacies, thereby enhancing the likelihood of building a robust and compliant HIPAA software solution.
2. Look for prior HIPAA-related projects
Check if your potential software partners handled HIPAA certification projects before. This highlights their expertise in navigating rigorous security and privacy standards and reflects their understanding of compliance and dedication to securing medical data.







